
What’s the Difference Between GPT and MBR When Partitioning a Drive?
Set up another plate on Windows 10 or 8.1 and you’ll be found out if you need to utilize MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table). Today we’re clarifying the contrast among GPT and MBR and assisting you with picking the right one for your PC or Mac.
GPT carries with it many benefits, yet MBR is as yet the most viable is as yet essential at times. This isn’t a Windows-just norm, coincidentally—Mac OS X, Linux, and other working frameworks can likewise utilize GPT.
A parcel structure characterizes how data is organized on the segment, where allotments start and end, and furthermore the code that is utilized during startup if a segment is bootable. In the event that you’ve at any point parceled and designed a plate—or set up a Mac to double boot Windows—you’ve probably needed to manage MBR and GPT. GPT is the new norm and is steadily supplanting MBR.
What Do GPT and MBR Do?
You need to parcel a plate drive before you can utilize it. MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two distinct methods of putting away the dividing data on a drive. This data incorporates where parcels start and end on the actual plate, so your working framework knows which areas have a place with each segment and which segment is bootable. This is the reason you need to pick MBR or GPT prior to making segments on a drive.
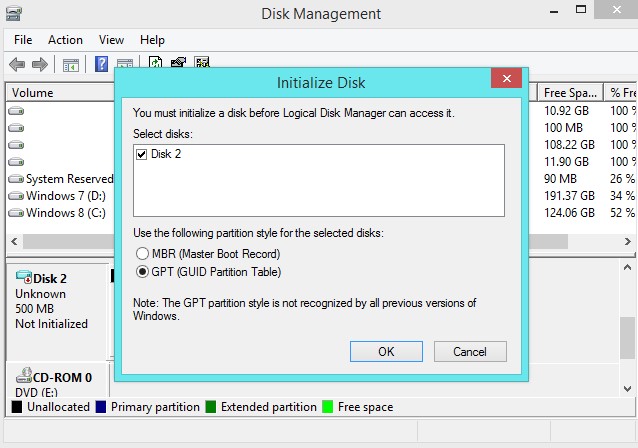
MBR’s Limitations
MBR was first presented with IBM PC DOS 2.0 in 1983. It’s called Master Boot Record on the grounds that the MBR is an uncommon boot area situated toward the start of a drive. This area contains a boot loader for the introduced working framework and data about the drive’s coherent allotments. The boot loader is a little digit of code that for the most part stacks the bigger boot loader from one more segment on a drive. On the off chance that you have Windows introduced, the underlying pieces of the Windows boot loader dwell here—that is the reason you might need to fix your MBR in case it’s overwritten and Windows will not begin. In the event that you have Linux introduced, the GRUB boot loader will normally be situated in the MBR.
MBR has its restrictions. First off, MBR just works with plates up to 2 TB in size. MBR likewise just backings up to four essential segments—assuming you need more, you need to make one of your essential parcels an “broadened segment” and make coherent segments inside it. This is a senseless little hack and shouldn’t be fundamental.
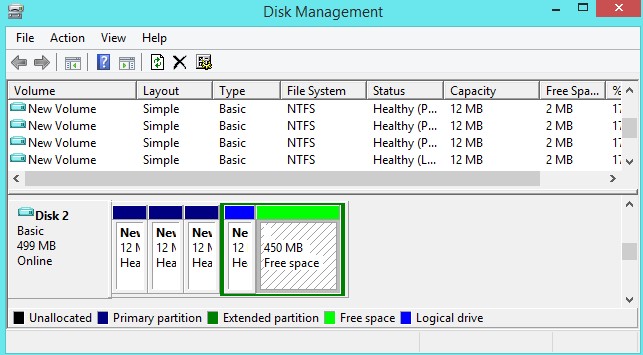
GPT’s Advantages
GPT represents GUID Partition Table. It’s another standard that is bit by bit supplanting MBR. It’s related with UEFI, which replaces the awkward old BIOS with something more current. GPT, thusly, replaces the awkward old MBR dividing framework with something more current. It’s called GUID Partition Table in light of the fact that each parcel on your drive has a “universally one of a kind identifier,” or GUID—an irregular string so long that each GPT segment on earth probably has its own exceptional identifier.
GPT doesn’t experience the ill effects of MBR’s cutoff points. GPT-based drives can be a lot bigger, with size limits reliant upon the working framework and its document frameworks. GPT likewise takes into consideration an almost limitless number of allotments. Once more, the cutoff here will be your working framework—Windows permits up to 128 parcels on a GPT drive, and you don’t need to make a drawn out segment to make them work.
On a MBR plate, the parceling and boot information is put away in one spot. In the event that this information is overwritten or defiled, you’re in a difficult situation. Conversely, GPT stores numerous duplicates of this information across the circle, so it’s considerably more powerful and can recuperate if the information is adulterated.
GPT additionally stores cyclic repetition check (CRC) qualities to make sure that its information is flawless. In the event that the information is undermined, GPT can see the issue and endeavor to recuperate the harmed information from one more area on the circle. MBR had no chance of knowing whether its information was debased—you’d possibly see there was an issue when the boot cycle fizzled or your drive’s parcels disappeared.
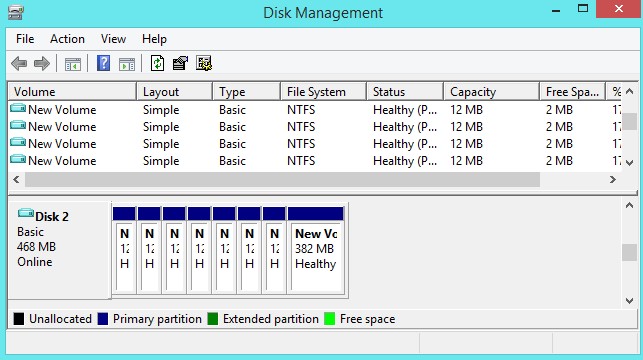
Compatibility
GPT drives will in general incorporate a “defensive MBR.” This sort of MBR says that the GPT drive has a solitary parcel that stretches out across the whole drive. On the off chance that you attempt to deal with a GPT plate with an old instrument that can just peruse MBRs, it will see a solitary segment that reaches out across the whole drive. This defensive MBR guarantees the old apparatuses will not confuse the GPT drive with an unpartitioned drive and overwrite its GPT information with another MBR. All in all, the defensive MBR shields the GPT information from being overwritten.
Windows can just boot from GPT on UEFI-based PCs running 64-bit adaptations of Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, and comparing server renditions. All renditions of Windows 10, 8, 7, and Vista can peruse GPT drives and use them for information—they can’t boot from them without UEFI.
Other current working frameworks can likewise utilize GPT. Linux has implicit help for GPT. Apple’s Intel Macs at this point don’t utilize Apple’s APT (Apple Partition Table) plan and use GPT all things considered.
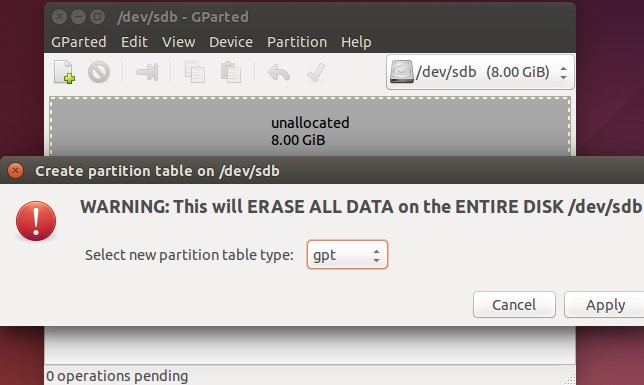
You’ll most likely need to utilize GPT when setting up a drive. It’s a more present-day, hearty standard that all PCs are advancing toward. On the off chance that you need similarity with old frameworks — for instance, the capacity to boot Windows off a drive on a PC with a conventional BIOS — you’ll need to stay with MBR for the time being.



